Blog
Welcome to FaceForward
Get the scoop on all things beauty, wellness, and skincare.
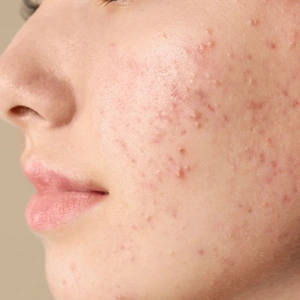
Frequent breakouts and painful acne bumps can be frustrating to treat, especially if you don’t know what kind of blemishes you’re dealing with.
Acne can range from mild to severe and must be properly identified to ensure that you receive the best acne treatment.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the key differences between two common types of breakouts: regular and cystic acne.
We’ve also included a list of tried-and-true treatment methods to help you treat blemishes and achieve healthy skin.
|
Summary
|
Acne—also known as acne vulgaris—is a skin condition that frequently occurs when impurities like oil, dirt, and dead skin cells become trapped in pores. Inflammation also plays a central role that is still being understood by dermatologists and researchers. For cystic acne, it may be the primary factor.
Most acne breakouts are caused by factors beyond our direct control, like hormonal changes and stress. These breakouts are also typically mild and can be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) skincare products. Acne also often resolves on its own.
Cystic acne is an inflammatory skin condition that causes painful pimples filled with pus—called cysts or sebaceous cysts—to develop deep beneath the surface of the skin.
It’s also regarded as the most severe form of acne.
Because cystic acne develops underneath the skin, it can be difficult to treat and may cause scarring. If you suspect that you may have cystic acne, it’s best to see a dermatologist. They will be able to recommend the right products and treatment options, and will also monitor your symptoms if you have to take prescription medicine.
It’s important to know what kind of breakout you’re dealing with as you seek treatment. This will help you make more informed decisions about the products you use to address your skin concerns.
Let’s take a closer look at the key differences between regular and cystic acne.
|
Formation |
Appearance |
Causes |
|
|
Regular acne |
Blemishes form on the surface of the skin when impurities become trapped in the pores or hair follicles. These blemishes usually aren’t painful. Breakouts also tend to be mild, meaning that only a handful of blemishes appear on the skin. |
Small red bumps all over the face. Blemishes may appear as blackheads or whiteheads and are often filled with pus. |
Excess sebum (oil) that builds up on the skin. An excess of oil is often caused by:
|
|
Cystic acne |
Bumps develop deep underneath the skin’s surface and form a cyst. Blemishes are normally painful and tender. |
Large red lumps—called cysts or sebaceous cysts— usually develop around the cheek, chin, and jaw area. A sebaceous cyst can also form on the chest, neck, and shoulders. Cysts may also be filled with pus or appear crusty. |
Bacterial infection that inflames existing blemishes. It can also develop due to:
|
If you’re concerned about the severity of your breakouts, it’s always recommended to speak to a dermatologist or licensed clinician.
Picking at or trying to pop cysts and pimples may increase the risk of acne scarring.
Squeezing a cyst or pimple forces pus out of the pore and often puts too much pressure on the tissue beneath the skin’s surface. When the tissue gets damaged, it can undergo a permanent change, and a scar develops. Opening up an acne cyst can also increase the risk of spreading the bacterial infection and making the breakout worse.
This may also lead to another skin condition called cellulitis—a painful infection that occurs in the tissue beneath the surface of the complexion that can cause cysts to swell. Cellulitis may make the skin more vulnerable to hyperpigmentation that can be difficult to fade.
The treatment options for cystic acne and regular breakouts differ slightly.
Cystic acne is a more severe condition that often requires strong prescription medication and other medical treatments.
Regular acne, on the other hand, can often be treated with OTC products and home remedies.
Topical treatments like the following are common and often effective for improving the appearance of mild to moderate forms of acne.
Clindamycin is an FDA-approved topical antibiotic that may be effective in reducing bacterial infections and healing existing blemishes.
It works by killing blemish-causing bacteria (frequently Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes)). This organism can also cause inflammation which can lead to painful red bumps.
Clindamycin also has anti-inflammatory properties that can reduce acne-related pain and swelling. These properties and the ability to kill harmful bacteria can help clindamycin prevent the formation of cystic acne.
Niacinamide is derived from vitamin B3 and can help reduce acne-related inflammation. It may also help improve the skin’s elasticity, too.
This ingredient is intended to slow cytokines, which can prompt unnecessary inflammatory responses. Inhibiting cytokines helps niacinamide reduce inflammation and minimize pain associated with acne. This can also help decrease redness and swelling.
Niacinamide may also be effective in regulating oil production, which can help prevent clogged pores.
Retinoids are powerful substances derived from vitamin A—a nutrient that’s well-known for its ability to help the complexion heal.
Retinoids, of which there are many, help the skin produce new cells while pushing oil, dirt, and other impurities from the pores. Not only does this clear and prevent clogged pores, but it can also help the skin rebuild damaged tissue to heal scarring.
Salicylic acid is a gentle exfoliating ingredient that may be effective in removing impurities and dissolving excess oil from the skin’s surface. This helps to unclog pores and prevent future breakouts.
Salicylic acid’s anti-inflammatory properties are also able to help reduce pain and swelling associated with acne.
Benzoyl peroxide is designed to fight acne by killing bacteria and pushing impurities from the pores. It also has anti-inflammatory properties.
This ingredient may be a good treatment option for cystic acne because benzoyl peroxide can reduce redness and swelling, and prevent bacterial infections.
Not only can this help reduce the appearance of inflamed blemishes, but it can also prevent new cysts from appearing and becoming infected.
Taking oral medication to treat acne is often reserved for severe cases—like cystic breakouts—or if you haven’t seen any results from using OTC treatments.
Birth control pills are a common FDA-approved medication that may help women to treat hormonal acne.
These medications work for acne by affecting hormone levels that increase sebum production and inflammation and contribute to acne.
Low-dose antibiotics may be effective in preventing bacteria that can infect existing blemishes. This can help heal acne and prevent future breakouts.
The most common antibiotics used for treating acne are:
Some antibiotics are also designed to prevent a buildup of oil on the skin which helps to reduce the risk of future breakouts.
Isotretinoin is a prescription-strength retinoid taken orally that is used for treating sebaceous cysts and other severe acne forms.
It not only speeds up skin healing but may shrink the sebaceous glands that produce oil to reduce the amount of sebum on the skin. This helps prevent clogged pores and clear severe acne. Isotretinoin is also intended to promote the production of new skin cells to replace dead ones. This may help the skin heal damaged tissue that can cause scarring.
Clinicians may also recommend clinical and aesthetic dermatology procedures to remove blemishes and prevent scarring.
These procedures are performed by a licensed skin aesthetician. Popular aesthetic treatments include:
If you suffer from cystic acne, a professional dermatologist can help assess the severity of your breakouts and determine the best treatment options.
At Nava MD, we know how challenging it can be to treat and heal breakouts—especially if you‘re struggling with severe acne.
That’s why we’ve made dermatologists and prescription acne treatments more accessible than ever with online visits and formulas mailed to your door.
Learn more and get started with an online dermatology visit today.
This article is intended for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice.
Consult a healthcare professional or call a doctor in the case of a medical emergency